
- Cybersecurity
- November 7, 2025
Table of Contents
Every great development is associated with some difficulties. With the advanced technological changes, cyber threats and privacy have become a frequent problem. The list of hackers is only increasing in skills; at this very moment you are reading this, a company somewhere might be the next to be attacked. According to expert projections, the number of vulnerabilities is bound to rise by 83 percent until 2025, and more than five vulnerabilities will arise every minute.
Living in the modern world means that technology is involved in every aspect of life, and cybersecurity is no longer a choice but an obligation. Everyone, from the youngest to the oldest, should know about the risk of cyber-attacks and how they can protect themselves. Read further to learn about the most important forms of cyber threats and how they can most effectively be used to keep yourself safe on the Internet.
Top 10 Types of Cyber Threats
You must know a few common types of cyber threats before moving towards the solution. To find an apt solution, one must know how to identify the problem. The list of different types of cyber threats is mentioned below.
1. Malware
The word ‘malware’ means ‘malicious software’, which is intentionally designed to harm or exploit systems. Hackers create malware to steal data, damage systems, and spy on users. It spreads through emails, infected websites, USBs, etc. Viruses, worms, trojans, and spyware are some types of malware.
2. Phishing
Phishing is a cyberattack in which attackers trick users into sharing their personal information by pretending to be a trusted entity. This personal information may include stuff like passwords, login credentials, ATM pins, etc. Attackers send a personal email to the victim. The email looks exactly like the official ones. These emails include an attachment or a link. Once the victim clicks on one, he/she unknowingly allow the attacker access to all the information.
3. Password Attack
A password attack is another form of cyber attack where attackers basically try to steal, break, or guess the password to have unauthorized access to accounts, systems, etc. Some forms of password attacks are brute force attacks, dictionary attacks, credential stuffing, keylogging, phishing for passwords, etc.
4. DoS and DDoS
- In a DoS attack, hackers flood the network or server with too much traffic, slow down the performance, and thereby make it unavailable to the actual users.
- In DDoS, hackers deluge servers with a lot of traffic, which brings down the site/app and leads to losses in revenue.
There exist three types of DoS and DDoS attacks: 1. Volume-based: Overwhelming with huge traffic. 2. Protocol-based: exploiting the server protocols 3. Application layer attacks: targeting certain apps or websites.
5. Man-in-the-Middle (MITM)
A man-in-the-middle attack occurs when the cybercriminal poses between the two parties without their knowledge. They act as a service representative for the individual and as an individual of the service providers. They happen to steal data like login credentials, personal information, etc.
6. Malvertising
In malvertising, the attacker uses digital ads to spread malware in order to make targets land on malicious websites. The ad looks like a normal marketing ad, but it contains bugs. Cybercriminals buy ad space on legitimate advertisement portals. If users click the ad, they may get directed to fake or look-alike websites.
7. Social Engineering
Social engineering refers to the psychological manipulation of the victim to give away all their personal information or perform any kind of action that compromises their security. Instead of attacking software, hackers attack human weaknesses like trust, fear, curiosity, etc. Social engineering can be performed in various ways, like phishing, spear phishing, baiting, etc.
8. Ransomware
Ransomware is an attack of cyber-extortion where access to a computer system is locked or encrypted. Instead, attackers ask the victim for ransom (money) in exchange for granting access again. Victims usually receive ransom notices asking for payment in cryptocurrency. At times, even when victims make payments, hackers fail to provide access back.
9. SQL Injection
SQL injection is an attack on web applications where malicious SQL code is passed into input fields by hackers to manipulate a database. The input fields are login forms, search fields, or URLs, or anything that will be helpful to gather information. It attacks applications that fail to validate or sanitize user input correctly. Hackers use poor coding in websites to gain entry to databases, and they harvest sensitive information such as customer data or financial data.
10. Advanced Persistent Threats (APTs)
An Advanced Persistent Threat (APT) is a sustained and focused cyberattack where hackers infiltrate a network and go undetected for a prolonged duration. Even months and years. APTs are financially well backed and organized, highly target-oriented, and aimed at espionage, data exfiltration, or sabotage rather than easy money.
The above-described cyber threats are the major ones. Apart from these, there are more cyber threats like cryptojacking and supply chain attacks. AI - powered attacks, etc. To understand the world of cyber threats, let us discuss recent conditions and a case study.
Current Status of Cyberthreat Cases
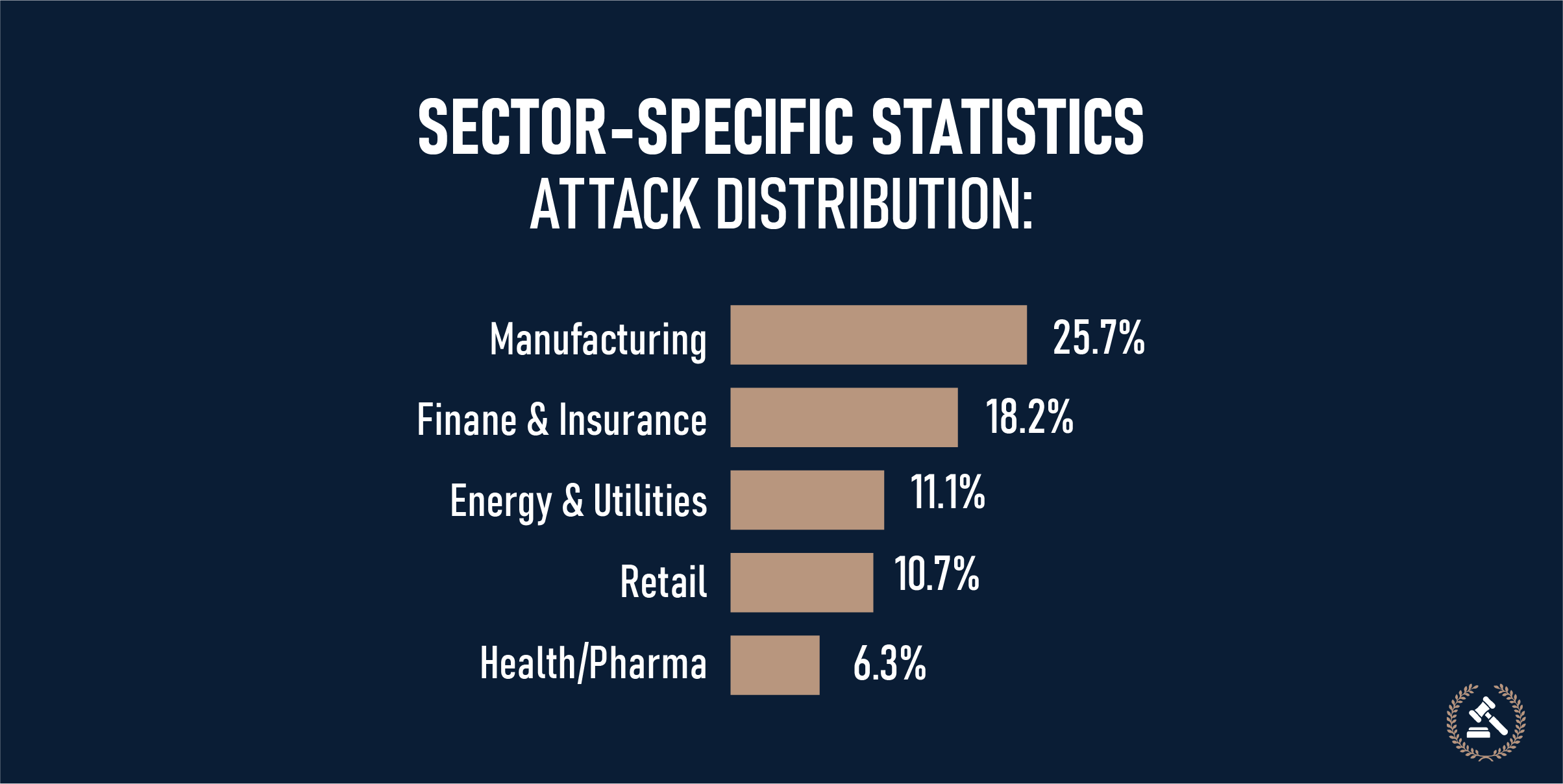
Increases in the cyberthreat cases:
There were 103 attacks reported in 2020. The number increased to 196 in 2024. As per the reports of Insurance Business America, the cases might reach 233 by the end of 2025. Phishing is dominant in 91% of successful breaches, and 38% of ransomware targeted the U.S. The following image depicts sector-specific data given by SQ Magazine.
Case Study of Ransomware Attack: A 158-year-old company was forced to shut down after a ransomware attack. According to Tom's HARDWARE, a UK-based transportation company with at least 158 years of history, has collapsed due to a ransomware attack. 700 people have lost their jobs due to money-grabbing cyberattackers, named as ‘Akira’ in a BBC report.
The internet-connected criminals are said to have gained access to KNP’s internet systems via a weak password that was used by one of the employees at the firm. After breaking this weakest link, the hackers encrypted and locked KNP’s operational data. The cyber villains then told KNP that the only way to get their data unlocked would be to pay.
A ransom note left by the hackers read as follows. “If you're reading this, it means the internal infrastructure of your company is fully or partially dead… Let's keep all the tears and resentment to ourselves and try to build a constructive dialogue,” says the BBC report.
After reading about the types and case studies of cyberthreats, the next immediate topic that comes to our mind is how we can protect ourselves or our companies from them. Keep reading further for the solutions.
Best Practices to Stay Safe
In most parts, businessmen and techies have found ways to avoid cyber threats using a variety of security measures.

- The installation of firewalls acts as the first line of defense in preventing cyberattacks. Firewalls control network traffic moving through the system and act to stop it if such an activity is suspect. Firewalls also include IDS/IPS, which monitors all network activities for unusual actions and blocks malicious attempts. In addition to this, network segmentation strengthens the security by dividing the network into small segments. It becomes difficult for a hacker to enter the system and move around.
- Antivirus and anti-malware software make sure that malware is detected and removed before damage can be brought into your system. Spam filters and anti-phishing tools help to avoid the risk of cyber dangers, while modern browsers already have built-in protectors that warn users in real time.
- One of the easiest, yet most effective, defenses against cyberattacks is simply keeping your systems up to date. Outdated software usually contains security gaps that hackers can use. Regular updates and appropriate patch management close these holes before the attackers can take advantage of them.
- Avoid clicking on suspicious links or downloading files from unknown sources. Always verify the sender’s identity and double-check URLs before opening them. Never share sensitive details over email or text, and only trust websites that use HTTPS. If your browser warns about an insecure certificate, don’t ignore it. Similarly, beware of sudden pop-ups offering downloads or “fixes.” Even oversharing on social media can make you a target for social engineering attacks.
- Data protection involves regular and secure backups. Data protection involves keeping backups. Secure and regular backups, whether offline or via the cloud, help you recover from ransomware or system crashes. Moving copies to more than one location adds further protection. In addition, clear incident response planning can enable businesses to recover quickly once incidents occur.
- Another powerful layer of security is multi-factor authentication. Instead of relying on a password, MFA requires two or more forms of verification, thus making it much harder for criminals to get in, even if one credential is compromised. At the same time, passwords themselves should be long, unique, and difficult to guess. A password manager will help generate and store them securely. Companies should use encryption and salting to securely store passwords, establishing lockout policies that block brute-force attempts.
- The Zero Trust model further reinforces security: by default, no user or device is to be trusted, and each connection should be verified. When on Wi-Fi, avoid using it from public networks, use VPN in conjunction, and make sure WPA2 or WPA3 encryption is enabled.
- Encryption of sensitive data at rest and in transit renders it useless to any attacker, even if accessed. Backups kept offsite or in the cloud, encrypted, ensure business continuity. A backup that is kept securely off-site or in the cloud prevents data integrity and confidentiality from being compromised. Even when attackers may have access to encrypted data, breaking encryption is very hard and often impossible in practice.
Other than these measures, using ad blockers also provides an extra layer of protection by reducing the risk of malvertising. Educate employees on cybersecurity threats and social engineering tactics. These practices will help to avoid the attack. If you are already a victim, you report to the authorities.
Cybersecurity is a Continuous Process
The threats change with each passing day. Prevention alone does not equate to safety; rather, it is about detection, response, and recoverability. Quick reporting in case of suspicious activity, coupled with well-placed incident response and disaster recovery planning, aids in minimizing damage. Digital forensics may also identify the root cause of an attack to lower the risk of experiencing such a thing again. Ultimately, cybersecurity is about being vigilant, prepared, and continuously improving one's defenses.
FAQs (Frequently Asked Questions)
The main types of cyberthreats are: Malware, Phishing, Password Attack, Man-in-the-Middle Attack, Malvertising, Social Engineering, Ransomware, etc.
Phishing cyberattacks are the most common in 2025.
E-mail phishing, Spear phishing, Whaling, Smishing, etc, are some examples of phishing attacks.
Yes, ransomware attacks are increasing in 2025 in both number and complexity.
Malware is a general term for any malicious software designed to harm, exploit, or gain unauthorized access to systems. Spyware is a specific type of malware that secretly monitors user activity and steals sensitive information.